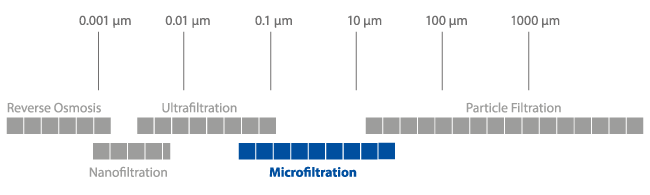
MICROFILTRATION INTRODUCTIONThe microfiltration process removes contaminants from fluids (e.g. liquids or gas) by flowing trough a microporous membrane. This method involves passing a fluid through a porous membrane or medium, which selectively retains particles and microorganisms above a certain size threshold. This is a purely physical (mechanical) separation process. The pore sizes of the membrane are from 0.1 to 10 μm. That means, the membrane retains all particles in the liquid or gas larger than the pore size. Other common filtration techniques, beside the microfiltration, are for example the ultrafiltration (pore size <0.1 μm) or nanofiltration. The filter itself, or the filter medium can have different shapes depending on the application requirements or the process. The most common variants are filter layers, candle filters, flat membranes, pocket filters or hollow fiber modules. Moreover, the filter surface can be made of materials like stainless steel, plastic, ceramic, textile fabric. The driving force in this processes is the differential pressure between inlet and outlet of the filter surface, which is between 0.1 and 10 bar. ApplicationsMicrofiltration is employed to achieve various filtration tasks across industries. The use of microfiltration allows the removal of fine solids and organisms e.g. bacteria in the sterile filtration step. Specially the beverage and water treatment industry uses this low pressure process for liquid purification. Other areas such as biotech use this filtration method for cell separation from fermentation broths. Also widely adopted is the microfiltration in industrial operations for tasks such as oil/water separation and the recovery of chemical cleaning agents. By leveraging microfiltration’s capability to selectively retain substances based on size, industries can efficiently extract oil from water, thereby facilitating environmentally friendly disposal or reuse. Moreover, the process enables the retrieval and reuse of valuable chemical cleaning agents, minimizing waste and enhancing cost-effectiveness in various manufacturing processes. Its adaptability and efficiency make microfiltration an essential tool in ensuring product quality and process integrity. In other words: this kind of filters are widely used where sterile product is required. |